How does Vitamin D affect our bodies?
Vitamin D is a crucial group of fat-soluble compounds responsible for enhancing the absorption of essential nutrients like calcium, iron, magnesium, phosphate, and zinc. In humans, the primary compounds in this group are vitamin D3 (also known as cholecalciferol) and vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol). While sunlight is the primary source of vitamin D, it can also be obtained through certain foods and supplements. Adequate levels of vitamin D are vital for maintaining bone health, supporting immune function, and regulating cell growth.
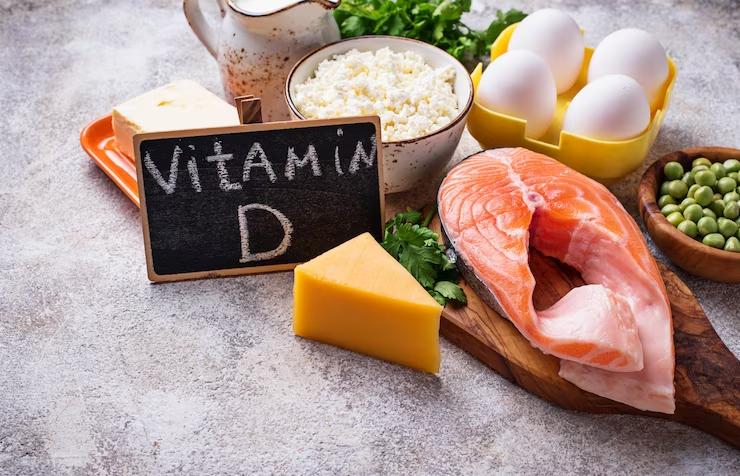

What are some effective ways to ensure I am getting enough Vitamin D?
To maintain healthy levels of Vitamin D, you can follow these strategies:
- Sunlight: Spend time outdoors, especially during midday, to allow your skin to produce Vitamin D when exposed to sunlight.
- Diet: Include Vitamin D-rich foods in your diet, such as fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, tuna), cheese, egg yolks, and fortified foods like milk, orange juice, and cereal.
- Supplements: If you struggle to get enough Vitamin D through sunlight and diet, consider taking Vitamin D supplements after consulting with a healthcare professional.
Remember to balance sun exposure for Vitamin D production with the need for sun protection to minimize the risk of skin cancer.
Top Sources of Vitamin D in Food
- Vitamin D is crucial for maintaining strong bones, supporting immune function, and aiding calcium absorption in the body. Consuming foods rich in this vitamin is essential for overall health. Here are some of the top sources of vitamin D in food:
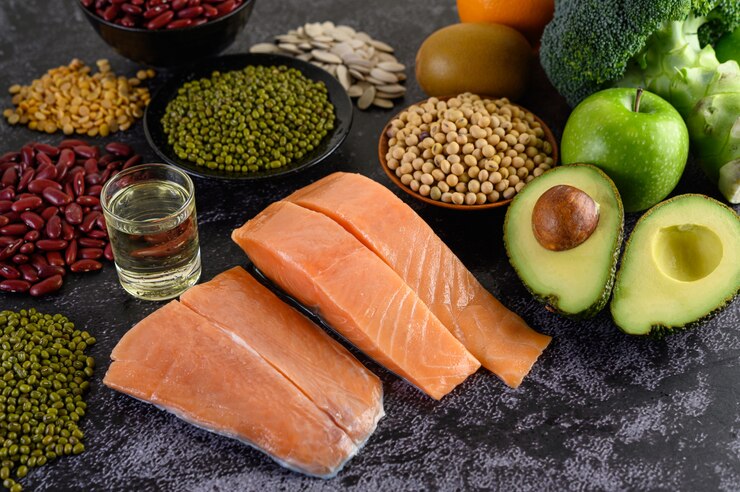

1. Fatty Fish: Salmon, trout, mackerel, and tuna are excellent sources of vitamin D.
2. Fortified Foods: Many foods such as milk, orange juice, and cereals are fortified with vitamin D.
3. Egg Yolks: Eggs, especially the yolks, contain a good amount of vitamin D.
4. Mushrooms: Some varieties of mushrooms, when exposed to ultraviolet light, can provide a decent amount of vitamin D.
5. Cod Liver Oil: This is a highly concentrated source of vitamin D.
Including these foods in your diet can help you meet your vitamin D requirements and support overall well-being.
Deficiency of Vitamin D
Vitamin D deficiency occurs when the body doesn’t receive enough exposure to sunlight or when it cannot absorb or metabolize the vitamin properly. This can lead to various health issues, including weakened bones, increased risk of fractures, and a higher susceptibility to infections.
To prevent deficiency, it’s important to ensure an adequate intake of vitamin D through sources like fatty fish, fortified dairy products, and supplements, as well as spending time in the sun. Regular check-ups and blood tests can help identify and address vitamin D deficiency in its early stages.