Overview:
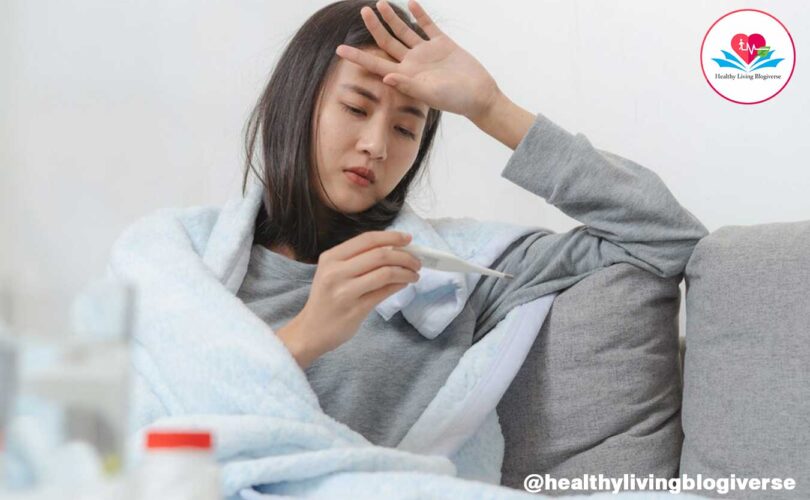
Typhoid is a bacterial infection caused by the bacterium Salmonella enterica serotype Typhi. It is a highly contagious disease that spreads through contaminated food and water or through close contact with an infected person.
Symptoms of typhoid include high fever, headache, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. If left untreated, it can lead to serious complications and even death.
- Typhoid can be prevented through proper sanitation and hygiene practices, like washing hands thoroughly and consuming clean and properly cooked food. Vaccines are also available to protect against typhoid. If you suspect you have typhoid, it is important to seek medical attention for diagnosis and treatment.
Symptoms of Typhoid
Typhoid fever is a serious bacterial infection caused by the bacterium Salmonella typhi. It is typically transmitted through contaminated food or water. Here are the common symptoms of typhoid:
- Fever: Sustained high fever, often reaching temperatures of 103-104°F (39-40°C), is a hallmark symptom of typhoid fever.
- Headache: Headaches are a common symptom and can range from mild to severe.
- Weakness and Fatigue: Persons with typhoid may often feel weak and exhausted, experiencing a lack of energy.
- Abdominal Pain: Generalized abdominal pain or discomfort may be present, especially in the area around the belly button.
- Loss of Appetite: Typhoid fever can cause a decreased desire to eat, resulting in a loss of appetite.
- Rose Spots: In some cases, small pink-colored spots, called rose spots, may appear on the abdomen and chest.
- Diarrhea or Constipation: Some individuals may experience diarrhea or constipation during the course of the illness.
- Cough: A dry cough can occur in some cases, although it is less common.
- Sweating: Profuse sweating, especially at night, is another symptom that may be observed.
- If you are experiencing these symptoms or suspect you may have typhoid fever, it is important to seek medical attention promptly.
- Typhoid fever can be treated with antibiotics, but early diagnosis is crucial for a full recovery.
Remember to practice good hygiene, such as handwashing, to help prevent the spread of typhoid and other illnesses.
Causes of Typhoid:
- Contaminated food and water: Typhoid bacteria are commonly found in food and water that has been contaminated with the feces of an infected person.
- Poor sanitation: Inadequate sanitation facilities and poor hygiene practices contribute to the spread of typhoid. Lack of proper sewage disposal and clean water supply increase the risk.
- Direct contact with infected individuals: Typhoid can spread through close contact with someone who is infected. This can happen when an infected person fails to practice proper hygiene and contaminates surfaces or objects.
- Travel to endemic areas: Traveling to regions where typhoid is prevalent increases the risk of acquiring the infection. Areas with limited access to clean water and sanitation facilities pose a higher risk.
Risk Factors of Typhoid
Here are some simple risk factors:
- Poor sanitation: Living in areas with bad sanitation and lack of clean water increases the risk.
- Contaminated food and drinks: Eating or drinking things that are not clean can cause infection.
- Close contact: Being near someone who already has typhoid can make it easier to get infected.
- Traveling to certain areas: Some places have more cases of typhoid, so if you travel there, you need to be careful.
- Not getting vaccinated: Not having the typhoid vaccine makes you more likely to get sick.
- Weak immune system: People with a weak immune system are more vulnerable to infections like typhoid.
Defeating Typhoid: Your Ultimate Prevention Guide
Typhoid fever is a serious and highly contagious bacterial infection caused by the bacterium Salmonella Typhi. To reduce the risk of contracting typhoid fever, it is important to take certain preventive measures. Here are some steps to help prevent typhoid:
- Vaccination: Getting vaccinated against typhoid fever is crucial, especially if you are planning to travel to areas where typhoid is endemic. There are two types of vaccines available: the injectable vaccine and the oral vaccine. Consult with a healthcare professional to determine which one is most suitable for you.
- Safe Food and Water: Contaminated food and water are major sources of typhoid infection. Follow these guidelines to ensure safe food and water consumption:
- Drink only bottled or boiled water. Avoid tap water and beverages with ice cubes.
- Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and clean water before eating or handling food.
- Consume only well-cooked, hot foods. Avoid eating raw or undercooked meats, seafood, and eggs.
- Peel fruits and vegetables yourself or consume cooked ones.
- Avoid street food and food from unreliable sources.
- Good Hygiene Practices: Practicing good hygiene can greatly reduce the risk of typhoid infection. Follow these hygiene measures:
- Wash your hands frequently with soap and clean water, especially before eating or preparing food, and after using the bathroom.
- Use hand sanitizers if soap is not available.
- Cover your mouth and nose with a tissue or your elbow when coughing or sneezing.
- Properly dispose of used tissues.
- Avoid close contact with individuals who have typhoid fever or those who are carriers of the bacteria.
- Sanitation and Hygienic Practices: Ensuring proper sanitation and hygienic practices in your surroundings can help prevent the spread of typhoid. Consider the following:
- Maintain clean and hygienic living conditions, particularly in kitchens and bathrooms.
- Regularly clean and disinfect surfaces and utensils that come into contact with food.
- Ensure proper sewage disposal and waste management.
 | Prevention is crucial in avoiding typhoid fever; by adhering to these guidelines, you can minimize the chances of contracting this disease, safeguarding yourself and those in your vicinity, thus if you suspect potential exposure or experience symptoms, it is essential to promptly seek medical care. |