Overview:
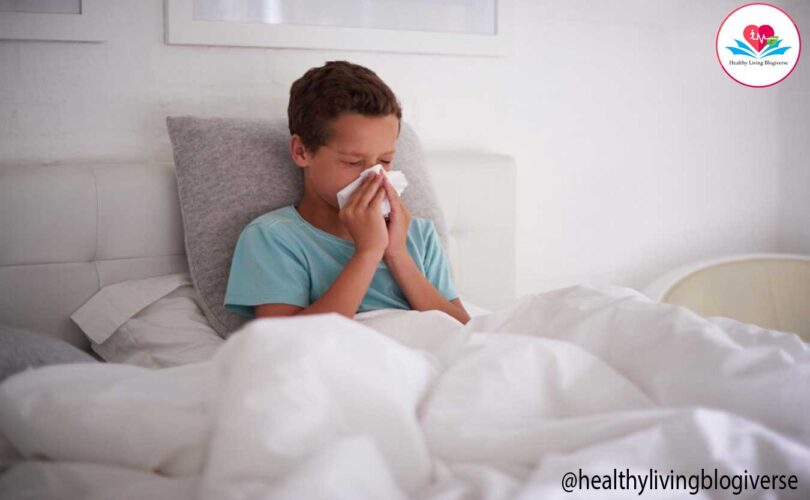
Pneumonia is a respiratory infection that can affect children. It causes inflammation in the lungs, making it difficult for them to breathe. Symptoms include coughing, rapid breathing, fever, chest pain, fatigue, and loss of appetite. If your child shows these signs, seek medical attention. Treatment depends on the cause and severity, usually involving antibiotics for bacterial pneumonia. To prevent pneumonia, ensure vaccinations, practice good hand hygiene, avoid smoke exposure, and encourage healthy habits. Consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Common symptoms of pneumonia in children:
- Cough: Children with pneumonia often have a persistent cough. The cough may be dry or produce phlegm.
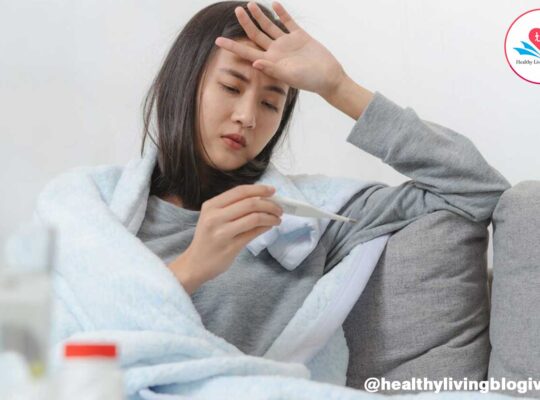
- Fever: A high fever is a common symptom of pneumonia. It may be accompanied by chills and sweating.
- Fast or difficult breathing: Children with pneumonia may breathe rapidly or have difficulty catching their breath. You may notice their chest sinking in or their nostrils flaring with each breath.
- Chest pain: Some children may complain of chest pain, especially when coughing or taking deep breaths.
- Fatigue: Pneumonia can make children feel tired or weak. They may lack energy and have less interest in usual activities.
- Loss of appetite: Children with pneumonia may have a decreased appetite and may refuse to eat or drink as usual.
- Vomiting: In some cases, children with pneumonia may vomit or have an upset stomach.
- Nasal congestion: While not as common as in colds, nasal congestion can also occur in children with pneumonia.
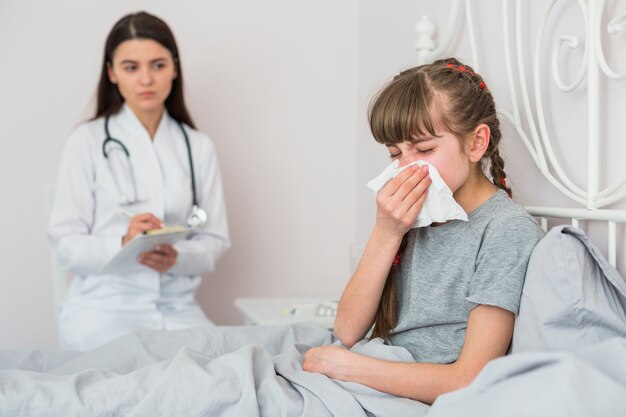

It’s important to note that these symptoms may vary depending on the age of the child and the specific type of pneumonia. If you suspect your child has pneumonia, it’s always best to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Managing Pneumonia in Children:
The general treatment approach for pneumonia in children includes the following steps:
- Diagnosis: A healthcare professional will evaluate the child’s symptoms, perform a physical examination, and may order diagnostic tests such as a chest X-ray or blood tests to confirm the presence of pneumonia.
- Antibiotics: If the pneumonia is caused by bacteria, the child will typically be prescribed antibiotics to fight the infection. It is important to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed by the healthcare provider, even if the child starts feeling better.
- Supportive Care: Along with antibiotics, supportive care is crucial for managing pneumonia in children. This may include:
- Fluids: Encouraging the child to drink plenty of fluids helps prevent dehydration and supports the immune system.
- Rest: Sufficient rest allows the body to recover and fight the infection effectively.
- Fever management: Fever-reducing medications recommended to help keep the child comfortable.
- Monitoring and Follow-up: It is important to closely monitor the child’s symptoms and ensure they are improving with treatment. Follow-up visits with a healthcare professional may be necessary to ensure complete recovery.
In severe cases of pneumonia, hospitalization may be required. This usually happens when a child is very young, has difficulty breathing, shows signs of dehydration, or has a weakened immune system. In the hospital, the child may receive intravenous antibiotics and additional respiratory support if needed.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and specific treatment plan for pneumonia in children.