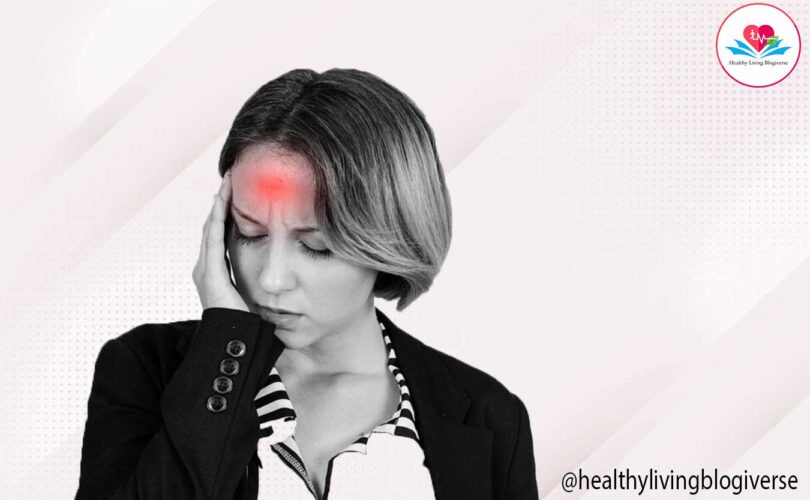
A migraine is a painful type of headache that is often characterized by a throbbing sensation on one side of the head. In addition to the head pain, individuals with migraines may experience nausea, sensitivity to light and sound, and in severe cases, vomiting. Migraines can last for a few hours to a few days. They can be triggered by various factors such as stress, certain foods, or inadequate sleep. If someone frequently experiences migraines or their migraines are particularly severe, it is advisable for them to consult a doctor. A doctor can provide assistance in managing pain, as well as offer strategies to prevent migraines from occurring.
Symptoms of Migraine
- Intense Headache: Migraine headaches are usually one-sided and pulsating, with moderate to severe pain that can last for hours or even days.
- Sensitivity to Light and Sound: Migraine sufferers often experience increased sensitivity to light (photophobia) and sound (phonophobia) during an attack. Bright lights and loud noises can exacerbate the headache.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Many people with migraines experience gastrointestinal symptoms like nausea and vomiting. These symptoms can sometimes precede or accompany the headache.
- Aura: Some individuals experience an “aura” before the onset of a migraine headache. Auras are usually visual disturbances but can also manifest as sensory changes or language difficulties. They typically last for less than an hour.
- Fatigue and Weakness: Migraine attacks can leave you feeling drained and fatigued. Some people may also experience muscle weakness or difficulty concentrating.
- Dizziness and Vertigo: Migraine attacks can cause a sense of dizziness or vertigo. You may feel unsteady on your feet or experience a spinning sensation.
- Tingling or Numbness: Some individuals may experience tingling or numbness in their face, hands, or other parts of the body during a migraine attack. This is known as a sensory aura.
- Difficulty with Vision: Migraines can affect your vision, causing temporary visual disturbances such as blurred vision, seeing flashing lights, or experiencing blind spots.
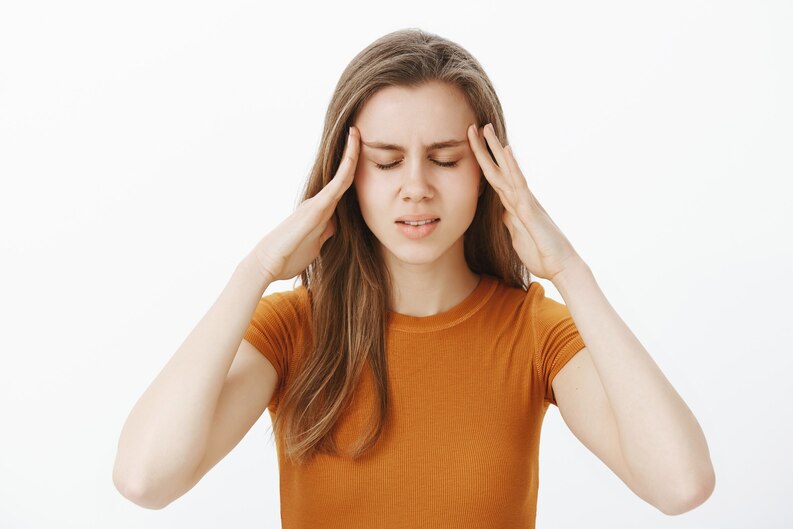

Migraine symptoms can vary from person to person and from episode to episode.
Causes of Migraine:
The common causes of migraines explained in a simpler way:
1. Genetic factors: Migraines can run in families, suggesting that there is a genetic link.
2. Hormonal changes: Fluctuations in hormones, especially estrogen, can trigger migraines. This is why some women experience migraines around their menstrual cycles.
3. Certain foods and drinks: Some foods and drinks, like cheese, chocolate, caffeine, and alcohol, can act as triggers for migraines in susceptible individuals.
4. Environmental factors: Bright lights, loud noises, strong smells, and even changes in weather can provoke migraines in some people.
5. Stress and emotions: Stress, anxiety, and intense emotions can bring on migraines.
6. Sleep disturbances: Lack of sleep or disruptions in sleep patterns can increase the risk of migraines.
Remember, these causes can vary from person to person, and not everyone will be affected by the same triggers. Consulting with a healthcare professional is recommended for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment options.
Risk factors of Migraine:
- Family history: If a close family member, such as a parent or sibling, has migraines, you may be more likely to develop them.
- Gender: Women are more likely to experience migraines than men.
- Hormonal changes: Hormonal fluctuations, particularly during the menstrual cycle or menopause, can trigger migraines in some individuals.
- Age: Migraines can occur at any age, but they tend to be most common during adolescence and early adulthood.
- Certain medications: Some medications, such as hormone replacement therapy or oral contraceptives, may increase the risk of migraines in certain individuals.
- Stress: High levels of stress or sudden changes in stress levels can contribute to the onset of migraines.
- Sleep disturbances: Both insufficient sleep and excessive sleep can be triggers for migraines.
- Environmental factors: Exposure to certain triggers like strong smells, bright lights, or loud noises can lead to migraines in susceptible individuals.
- Dietary factors: Consuming certain foods and drinks, such as aged cheeses, chocolate, alcohol, and caffeine, can sometimes trigger migraines.
- Weather changes: Fluctuations in weather conditions, such as changes in barometric pressure or temperature, may trigger migraines in some individuals.
Preventive Tips for Migraine: Effective Strategies to Manage and Minimize Symptoms
Migraines can be debilitating and interfere with daily life. While there is no cure for migraines, there are several preventive measures that can help reduce the frequency and severity of these headaches. Here are some tips to consider:
- Identify and avoid triggers: Keep a migraine diary to identify triggers that may be causing your headaches. Common triggers include certain foods (such as chocolate, caffeine, and processed foods), alcohol, stress, hormonal changes, bright lights, strong smells, and changes in sleep patterns. Once you identify your triggers, try to avoid or minimize your exposure to them.
- Establish a regular sleep schedule: Getting enough sleep on a regular basis can help prevent migraines. Aim for 7-8 hours of quality sleep each night and try to maintain a consistent sleep schedule. Avoid oversleeping on weekends or having irregular sleeping patterns, as this can trigger migraines.
- Manage stress: Stress is a common trigger for migraines. Find healthy ways to manage and reduce stress in your life. This could include practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, yoga, or engaging in activities that you enjoy.
- Stay hydrated: Dehydration can trigger migraines in some individuals. Make sure to drink enough water throughout the day and stay hydrated. Avoid excessive intake of caffeine or alcohol, as they can cause dehydration.
- Exercise regularly: Engaging in regular physical activity can help reduce the frequency and intensity of migraines. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise, such as walking, swimming, or cycling, on most days of the week.
- Maintain a healthy diet: Eating a well-balanced diet can play a role in preventing migraines. Include plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins in your meals. Avoid or limit processed foods, artificial sweeteners, and foods that may be triggers for you.
- Consider supplements or medications: In some cases, your healthcare provider may recommend certain supplements or medications to help prevent migraines. These could include magnesium, riboflavin (vitamin B2), coenzyme Q10, or prescription medications specifically designed for migraine prevention. Consult with your doctor before starting any new supplements or medications.
Treatment Options for Migraines
1. Lifestyle changes: Making certain changes in your daily habits can help reduce migraine frequency and severity. This may include regular exercise, getting enough sleep, managing stress, and avoiding triggers such as certain foods or environmental factors.
2. Over-the-counter pain relievers: For mild to moderate migraines, non-prescription pain medications can often provide relief.
3. Prescription medications: If over-the-counter options don’t sufficiently relieve your migraines, your doctor may prescribe medications specifically designed to treat migraines. These include triptans, which help relieve pain and reduce inflammation, or preventive medications to reduce the frequency and severity of migraines.
4. Botox injections: In some cases, Botox injections may be recommended for chronic migraines. This treatment involves injecting Botox into specific muscles of the head and neck to help prevent migraines.
5. Alternative therapies: Some people find relief from migraines through alternative therapies such as acupuncture, biofeedback, or relaxation techniques. These methods may be used alone or in combination with other treatment options.
Remember, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment for your individual situation. They can assess your condition and develop a personalized treatment plan tailored to your needs.