Overview:
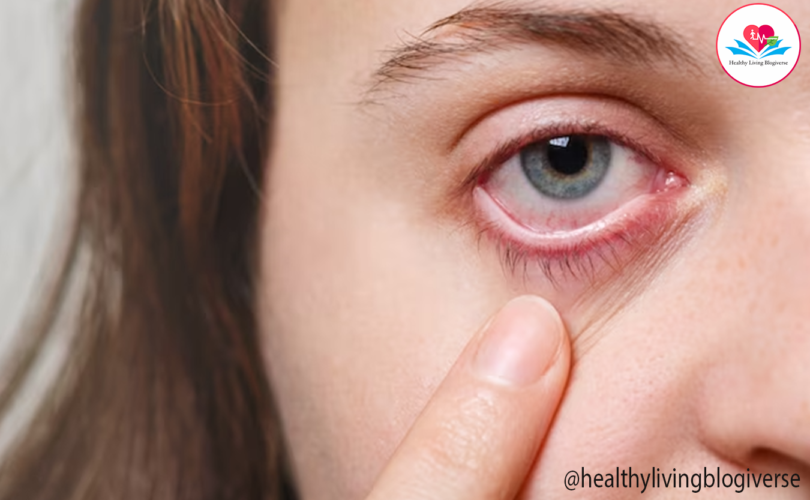
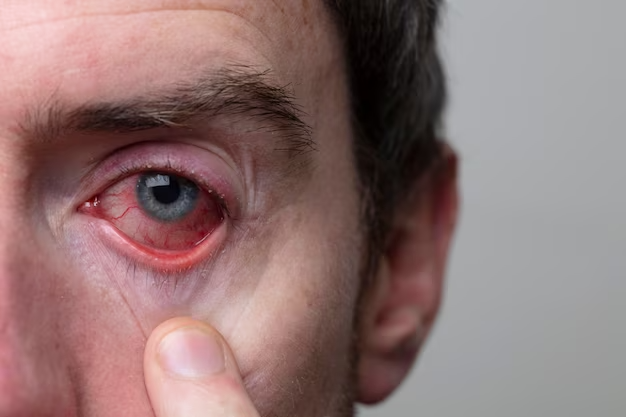
Conjunctivitis—often referred to as pink eye—is an inflammation or infection of the transparent membrane (conjunctiva) that lines your eyelid and covers the white part of your eyeball. When small blood vessels in the conjunctiva become inflamed, they’re more visible. This is what causes the whites of your eyes to appear reddish or pink. Symptoms may include eye redness, itchiness, tearing, a gritty feeling in one eye or both eyes, and a discharge that forms a crust during the night that may prevent your eyes from opening in the morning. Conjunctivitis can be caused by a bacterial or viral infection, an allergic reaction, or in babies, an incompletely opened tear duct.
- Because conjunctivitis can be contagious, early diagnosis and treatment can help limit its spread.
- Washing hands frequently, avoiding touching the eyes, and using clean towels and washcloths are important preventive measures.
- It’s recommended to see a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment, which may include:
- Antibiotic drops for bacterial conjunctivitis.
- Other interventions for the allergic or irritant types.
Symptoms of Conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis, commonly known as pink eye, is an inflammation or infection of the transparent membrane (conjunctiva) that lines your eyelid and covers the white part of your eyeball. When small blood vessels in the conjunctiva become inflamed, they’re more visible. This is what causes the whites of your eyes to appear reddish or pink.
Symptoms of Conjunctivitis may include:
- Redness in one or both eyes
- Itchiness in one or both eyes
- A gritty feeling in one or both eyes
- A discharge in one or both eyes that forms a crust during the night that may prevent your eye or eyes from opening in the morning
- Tearing
People with conjunctivitis may also experience:
- Burning sensation in the eyes
- Blurred vision when the discharge from the eyes accumulates
- Increased sensitivity to light
Causes of Conjunctivitis:
It’s important to note that symptoms can vary depending on the cause of conjunctivitis. Conjunctivitis can be caused by:
- Viral infections, which are the most common cause and are highly contagious.
- Bacterial infections, which can also spread easily, typically causing more eye discharge.
- Allergens, such as pollen, dust, and pet dander which cause allergic conjunctivitis.
- Irritants, such as smoke, chlorine and certain chemicals.
If you exhibit symptoms of conjunctivitis, it’s advisable to seek medical attention as treatment may vary based on the cause. For bacterial cases, antibiotic eye drops or ointments may be prescribed. For viral and allergic cases, other medications may be recommended to relieve the symptoms, and many cases resolve on their own without requiring medical treatment.
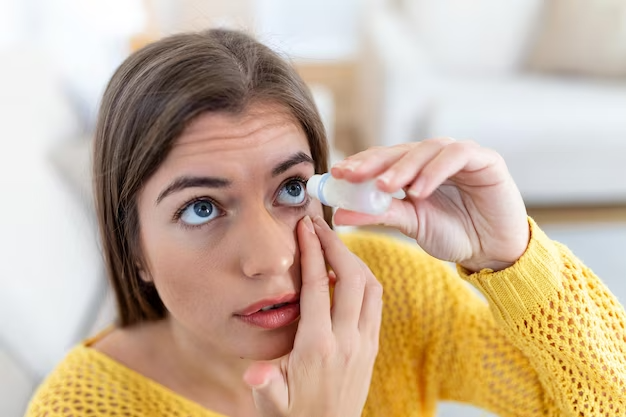

Preventive Measures of Conjunctivitis
Preventive measures for conjunctivitis can significantly reduce the risk of getting or spreading the infection. Here are some effective strategies:
Personal Hygiene
- Wash your hands frequently with soap and warm water for at least 20 seconds, especially before and after touching your eyes or face, and after applying eye drops or ointment.
- Avoid touching your eyes to prevent potential spread of the infection.
Avoid Sharing Personal Items
- Do not share personal items such as towels, washcloths, makeup, or eye drops with others.
Cleanliness
- Change towels and linens frequently, and wash them in hot water and detergent.
Contact Lens Care
- Follow proper contact lens care, including hand washing before handling lenses and following your eye care specialist’s instructions for cleaning and replacing lenses.
Protect Against Allergens
- If conjunctivitis is caused by allergies, try to reduce exposure to the allergen(s), such as pollen, dust, or pet dander.
Staying Home
- If you or your child has infectious conjunctivitis, avoid going to school or work until you no longer have symptoms or you have followed your doctor’s recommendations regarding treatment and recovery.
Avoid Smoke and Chemicals
- Protect your eyes from smoke, fumes, and other irritants that can cause inflammation and exacerbate symptoms.
Educate Family and Friends
- Teach others, especially children, the importance of not sharing items that touch the eyes, as well as the significance of thorough handwashing.
By adhering to these preventive measures, you can help control the spread of conjunctivitis and protect yourself and others from getting infected. If you suspect you have conjunctivitis, seek medical advice to determine the cause and appropriate treatment.